Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is the 11th most common cancer globally. In 2018, there were 458,918 new cases and 432,242 deaths worldwide.
Types Of Pancreatic Cancer
There are various ways in which a doctor or a specialist of cancer may classify pancreatic cancer:
Based on the cells that cancer originates from:
Adenocarcinoma: It is the most common type of pancreatic cancer that arises from cells lining the ducts (hollow tubes) of the pancreas.
Cystic tumours: This type of cancer leads to the development of a fluid-filled sac called a cyst.
Acinar cell cancer: This type of cancer develops in the acinar cells, which lie at the ends of the ducts that produce enzymes.
Based on the spread of cancer
Localised pancreatic cancer: The cancer is contained within the pancreas and has not spread anywhere else in the body.
Locally advanced pancreatic cancer: The cancer has spread to the tissues around the pancreas, to the nearby lymph nodes, or nearby blood vessels, but has not spread to other parts of the body.
Metastatic pancreatic cancer: The cancer has spread to another part or parts of the body, also known as metastases.
Staging Of Pancreatic Cancer
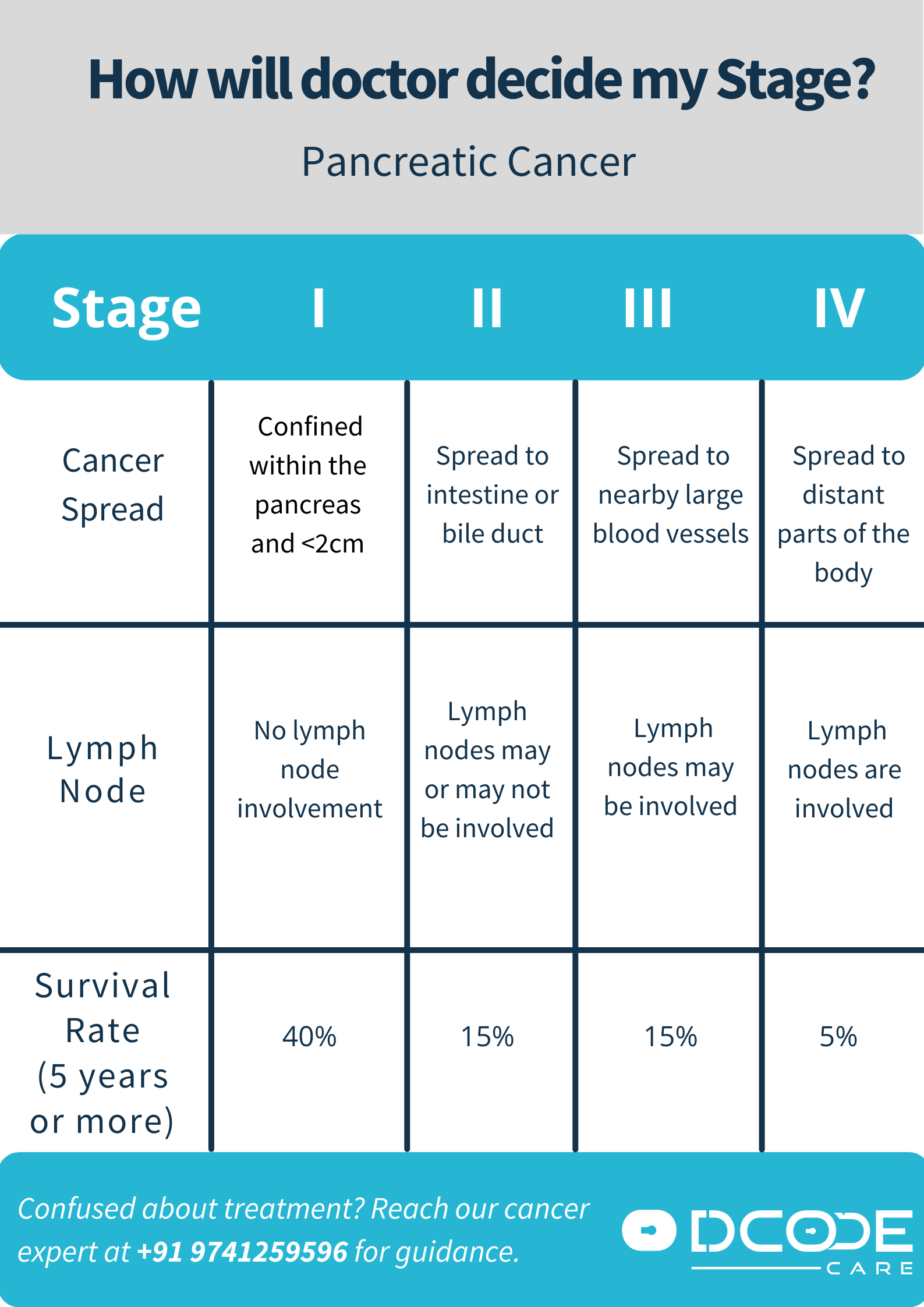
If you are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, doctors that treat cancer will run more tests to determine the extent (stage) of your cancer. The stage of your cancer is based on the size and spread of the tumour and helps your doctor or specialist of cancer decide which treatments are optimum.
- Stage 0: Cancer is confined to the top layers of pancreatic duct cells and sometimes referred to as carcinoma in situ.
- Stage I: Cancer restricted to the pancreas with no spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. It has two sub-stages: Stage IA (The cancer is confined to the pancreas and is no bigger than 2 cm across), Stage IB (The cancer is confined to the pancreas and is larger than 2 cm (0.8 inches) but no more than 4 cm across)
- Stage II: The cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes with no spread to distant organs. It has two sub stages. Stage IIA (Cancer is confined to the pancreas and is bigger than 4 cm across) Stage IIB (Cancer is confined to the pancreas and is less than 2 cm across and has spread to 1 to 3 nearby lymph nodes OR is 2-4 cm across and has spread to 1-3 lymph nodes OR is larger than 4 cm and has spread to 1-3 lymph nodes).
- Stage III: The cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes with no spread to distant organs. It may be less than 2 cm and spread to 4 or more lymph nodes OR is 2-4 cm across and has spread to 4 or more lymph nodes OR has grown outside the pancreas to nearby blood vessels.
- Stage IV: The cancer has spread to distant sites such as the liver, the lining of the abdominal cavity, the lungs or the bones.
Sources: Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018; European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) ; American Cancer Society