Breast Cancer
Breast cancer originates from the tissues of the breast, which maybe in the tubes that transport milk toward the nipple (ducts) or in the glands that make milk (lobule).
Breast cancer incidence has been increasing in India and is now the most common cancer in large cities in India, and the second most common in the rural parts of the country.
Types and Subtypes
For effective breast cancer management, we need to understand how a doctor for breast cancer classifies the conditions. They are as follows:
- Invasive vs Non-invasive: Defined based on whether the cancer cells are in the ducts only (non-invasive) or involve both the ducts and healthy breast tissue (invasive). Non-invasive cancer is called a pre-malignant lesion, meaning that it is not yet cancer but can progress to the invasive form.
- Early, Locally-advanced, Metastatic, Advanced: Early breast cancer is when the tumor has not spread beyond the breast or axillary lymph nodes. If it has spread to nearby tissue or lymph nodes it is locally advanced. Metastatic is when it has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs or bones. Advanced is the late stage of breast cancer, which maybe locally-advanced inoperable breast cancer and metastatic breast cancer.
- Other classifications done by a specialist for breast cancer could be based on hormone receptors and gene expression: If the growth of the tumors is stimulated by the hormones oestrogen and progesterone, the clinician will want to test for oestrogen receptor (ER) or progesterone receptor (PgR) activity. This is an indication for specific hormonal therapies. HER2 is a receptor that is involved in the growth of cells and is present in about 20% of breast cancers. HER2 positive tumor's is treated with specific types of chemotherapy
Staging of Breast Cancer
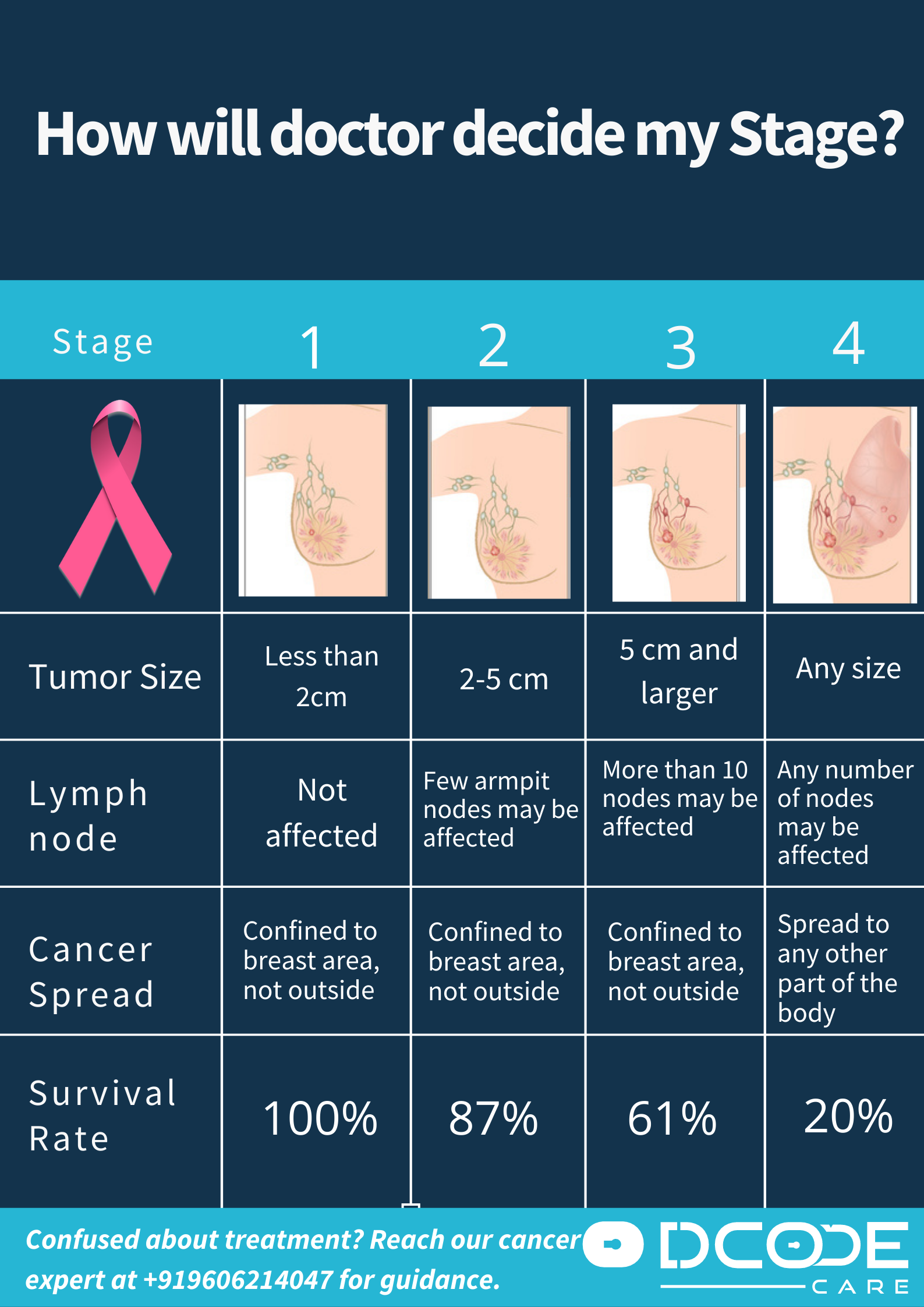
Once you are diagnosed, better medical management for breast cancer will include running more tests to determine the extent (stage) of your cancer. Your cancer's stage is an important input in deciding on your treatment. The stage of a cancer describes the size of the cancer and how far it has spread. It may be described as stage 0 to stage 4 and takes into account: the size of the cancer, whether the lymph nodes are affected, if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Stage 0: In this stage the cancer is limited only to the inside of the milk duct and the treatment is more conservative than invasive breast cancer.
- Stage 1: It is divided into two groups. Stage 1A (the cancer is 2cm or smaller and hasn’t spread outside the breast) Stage 1B (No cancer seen in the breast, but a few cancer cells found in the lymph nodes under the arm or the cancer in the breast is 2cm or smaller, and a few cancer cells found in the lymph nodes)
- Stage 2: It is divided into two groups. Stage 2A (No cancer seen in the breast or cancer smaller than 2cm but with spread to one to three lymph nodes or a tumour between 2-5 cm with no spread), Stage 2B (The tumour is between 2 to 5 cm with spread to the lymph nodes or larger than 5cm with no spread to the lymph nodes)
- Stage 3: It is divided into three groups. Stage 3A (No cancer in the breast, but cancer present in four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone; a tumour less than 5 cm with spread to four to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breastbone or breast tumour larger than 5 cm which has spread to up to three lymph nodes). Stage 3B (a tumour of any size that has spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall. Cancer is found in up to nine lymph nodes under the arm or near the breast bone. Stage 3C (tumour in the breast of any size, may have spread to the skin of the breast or chest wall and cancer is found in 10 or more lymph nodes)
- Stage 4: It is also known as secondary breast cancer. The cancer has spread (also known as metastasised) to other parts of the body. The spread may be to distant lymph nodes, lungs, bones, liver or the brain.
Sources: European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO); Breast Cancer India; Breast Cancer Care UK; American Cancer Society
Additional Videos
Here are some additional videos you might find useful.